©Courtesy of the Global Center of Adaptation and Aumsat Technologies
Issue
India’s acute water scarcity, aggravated by climate change, creates a pressing need for reliable and efficient solutions for sustainable management and equitable distribution of water resources.
Conventional water-finding methods are outdated and unreliable, creating an urgent need for innovative, precise, and scalable water management solutions. Solutions also must be widely available, and their cost should not hinder their use.
Solution
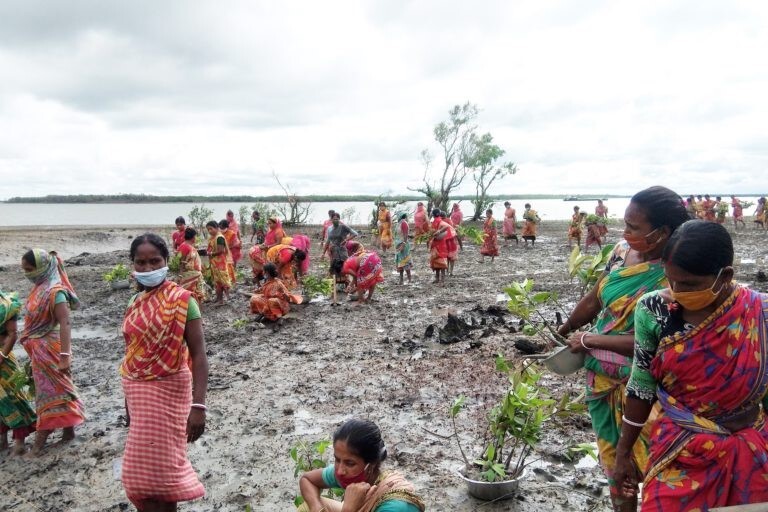
Aumsat, initially used to find water on the moon, was adapted for usage on Earth. It applies satellite-based radar analytics in a remote system that locates underground water and detects pipeline leaks, fostering efficient water use and conservation. With around 4,000 client stakeholders, a project to expand Aumsat use is underway in drought-affected Indian states.
Overview
In India, Aumsat Technologies is using remotely operated satellite radar analytics to pioneer water management solutions. Its namesake device, first developed for the Chandrayaan-2 lunar mission, can uncover water sources 60 meters deep and pipeline leaks with 90% accuracy.
Especially in drought-hit areas, this innovation offers an alternative to traditional but erratic methods like dowsing. Aumsat, a strong example of locally led adaptation, enhances resource management and supports sustainable agricultural practices amid climate change-induced water scarcity. It’s received the Local Adaptation Champions Award (Business Adaptation Solutions category) from the Global Center on Adaptation(GCA) and been emulated in other countries. Also, as it continues to develop and be recognized, it’s attracting more work orders and incorporated advanced technology such as JAXA space radar data.
Details

©Courtesy of the Global Center of Adaptation and Aumsat Technologies
Aumsat Technologies (Mumbai, India) has taken an innovative approach to tackling water scarcity in India using satellite radar analytics. The system is revolutionizing water management by accurately locating underground water sources up to 60 meters deep and identifying pipeline leaks deep within thick concrete. In this way, it both finds and conserves water.
Aumsat Technologies CEO Riddhish Soni leveraged his experience developing the system for the Chandrayaan-2 lunar mission, where it was used to find traces of water on the moon. He realized the potential of applying this space technology to address pressing issues on Earth, starting with water supply in his own country.
Aumsat operates remotely, allowing efficient assessment of vast land areas. This capability is particularly beneficial in India’s diverse and expansive landscapes, which suffer from droughts tied to climate change. Aumsat is helping ensure that water resources are managed effectively, even in remote or inaccessible areas. Previously, many people in such regions used traditional but unpredictable methods such as dowsing – relying on the movement of a stick or a coconut to lead to water.
Nearly 4,000 stakeholders and broad investment

©Courtesy of the Global Center of Adaptation and Aumsat Technologies
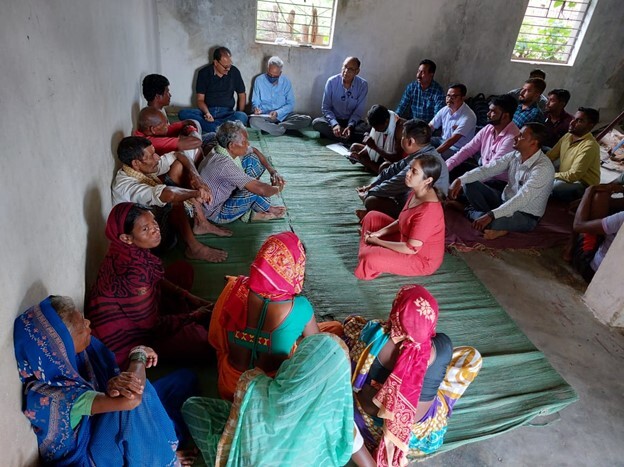
The system was piloted successfully in water-scarce areas and earned the support of NGOs and Indian ministries. Now, with almost 4,000 stakeholders, the ongoing Aumsat project was awarded the Local Adaptation Champions Award (Business Adaptation Solutions category) presented by the Global Center on Adaptation(GCA). The prize money from the award, along with Adaptation Fund sponsorship chances, will be used to bolster the analytics and work for equitable distribution of water.
With Aumsat’s business model, users pay a per-hectare annual fee to access a web-based platform and analytical services, which facilitate precision farming and smart-resilient agriculture. The technology’s accuracy and reliability fostered partnerships with local governments and NGOs, integrating Aumsat’s findings into urban planning and rural water resource management.
In this sense, Aumsat is an excellent example of locally led adaptation (LLA), where local knowledge and expertise are pivotal. Aumsat emphasizes community involvement and tailored solutions to local climate challenges. The LLA approach ensures the sustainability and effectiveness of adaptation measures and empowers communities, making them active participants in climate action efforts.
The collaborative approach has amplified the technology’s impact, increasing access to potable water, improving agricultural opportunities, and ultimately helping lower-income people toward a more sustainable future.
A sustainable, replicable model that keeps expanding
“We collaborate to integrate our findings into urban planning and rural water resource management,” Soni explains. This approach addresses immediate needs for water and builds resilience against the unpredictable nature of climate change. Aumsat’s success has also led to replication in countries like Afghanistan, Uganda, and Mauritius, evidencing its global applicability and potential.
The Aumsat system continues to attract stakeholders and accolades. It was recognized in the Government of India’s National Startup Awards, and prominent organizations such as the SELCO Foundation, Acumen, and IndusInd Bank have come onboard as collaborators. Aumsat is also now incorporating space radar data from the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) after being awarded by the agency in S-Booster 2022. After receiving the Local Adaptation Champions Award, Aumsat has been selected as the winner of the Imagine H2O 2024 cohort, the largest water technology competition organized by the Singaporean Government.
As Aumsat is increasingly integrated with local irrigation planning, the technology will continue to develop, offering hope for a sustainable and equitable water supply where it’s most needed and worldwide.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We extend our appreciation to the Global Center on Adaptation (GCA) for their generous provision of this case study to the database.
Related Information
KEYWORDS
- # Case Study
- # Agriculture
- # Life of Citizenry and Urban Life
- # Water Environment/Water Resources
- # Adaptation Action/implementation
- # Adaptation Business
- # Adaptation Planning/Policy
- # Education/Awareness/Information
- # International Cooperation
- # Locally-led Adaptation
- # Research/Innovation
- # Asia
- # India