Photo: Pixabay/koachphillips
Location
Coastal areas in Bangladesh
Bangladesh is located on the deltaic plain of the Ganges-Brahmaputra-Meghna (GBM) river network, which is low-lying. The target areas of this project are the coastal areas of Bangladesh, namely Khulna, Patuakhali, Chittagong, Barisal, and Noakhali regions. In these areas, people made their living by agriculture and fishing.
Issue
Decreasing coastal arable lands and food insecurity
The coastal areas of Bangladesh were highly vulnerable to sea level rise and frequent flooding. In the Khulna, Patuakhali, Chittagong, Barisal, and Noakhali regions targeted by this project, the cultivable area in the coastal zone has been shrinking year by year, mainly due to the effects of salinity, and this has created problems in terms of food security and sustainability of the people's livelihood. Thus, the risk of disasters combined with the medium- and long-term impacts of potential sea level rise and coastal erosion required adaptation measures to cope with them.
Solution / Lesson learned
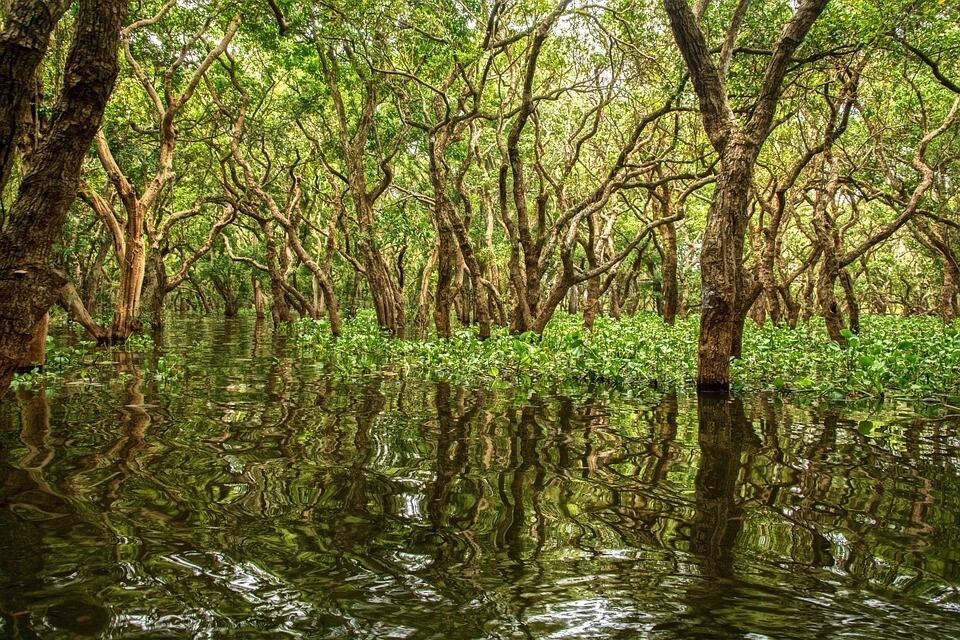
Restoring mangrove forests for climate resilience and people’s livelihoods
The Community-Based Adaptation to Climate Change through Coastal Afforestation (CBACC-CF) program is funded by the GEF-UNDP and implemented by the Bangladesh government. It has established 9,650 hectares of mangrove plantation, which absorbs more than 965,000 tonnes of carbon annually. These mangrove forests have not only mitigated disaster risks and the direct and indirect effects of climate change but have also contributed to diversifying the population's livelihoods by creating fishing opportunities. The mangrove forest plantations were carried out in an inclusive manner, avoiding landowner conflicts.
Related Information
KEYWORDS
- # Case Study
- # Agriculture
- # Coastal Areas
- # Fisheries
- # Forests/Forestry
- # Local Communities
- # Natural Disasters
- # Adaptation Action/implementation
- # Adaptation Funding/Finance
- # Climate Mitigation Co-Benefits
- # Disaster Prevention/Disaster Mitigation
- # Locally-led Adaptation
- # Nature-based Solutions
- # Asia
- # Bangladesh