LocationI
Maharashtra, India
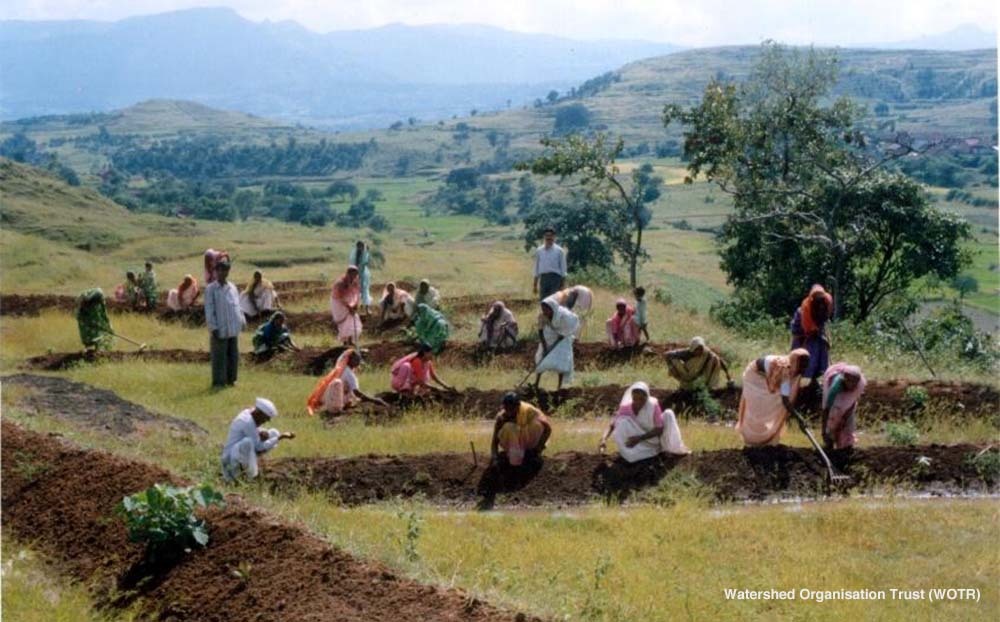
Maharashtra is a state in the western peninsular region of India. It has the second-highest population in India, comprising 6 divisions and 36 districts. While it is the most industrialized state in India, more than half of the population lives in the rural part. Those in rural areas typically engage with agriculture, with staples such as rice and millet as the main monsoon crops. They also grow cash crops such as sugarcane, cotton, oilseeds, and tobacco.
Issue
Maharashtra state faced with repeated droughts due to climate change
Maharashtra is facing repeated droughts due to climate change, which triggers crop failure and farmer suicides. The Maharashtra Groundwater Act, which regulates the management of groundwater used for domestic and agricultural purposes, is in place. However, the actual local governance to enforce such regulations has been insufficient. In the end, groundwater was considered private property and was over-utilized, which led to land degradation and other environmental degradation.
Solution / Lesson learned
Enhanced governance of groundwater thanks to the Water Stewardship Initiative
Seeing the lack of local governance as the cause, Watershed Organization Trust launched the Water Stewardship Initiative to build effective, efficient, and transparent governance. The Initiative targeted 100 rural villages in Maharashtra and undertook several initiatives to improve groundwater management. First, a water health chart was created in each village to visualize the groundwater status. In addition, a Village Water Management Team was created to carry out water management with reference to the chart. This team also conducted water budgeting for the planned operation of resources and educated the public about water conservation mechanisms. Through these efforts, the local governance structure for properly implementing the Maharashtra Groundwater Act was improved.