Photo: Pixabay/ejakob
Location
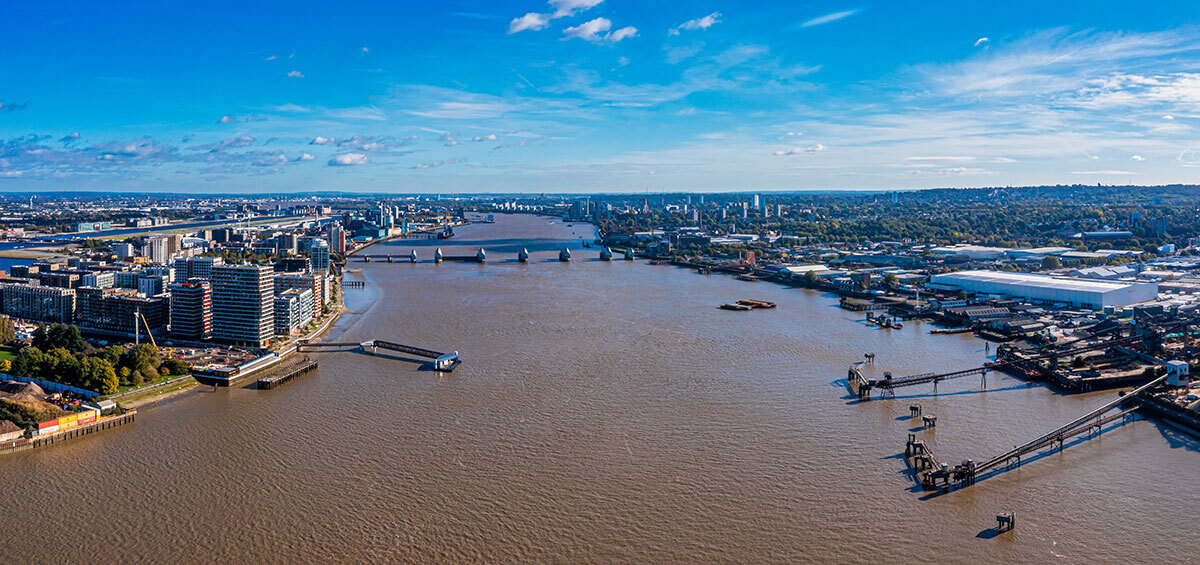
About Kerala, India
Kerala is a state located in the southern part of India. The Killiyar River, the main tributary of the Karamana River, originates at Theerthankara. The climate is tropical coastal and known for its high rainfall. The rainfall is caused by the southwest monsoon in summer and the northeast monsoon in winter.
Issue
High risk of floods and landslides in Kerala
Kerala's river basins are frequently affected by floods and landslides due to its rainy climate. For instance, the August 2018 disaster is considered the worst since 1924, with 341 landslides in 10 districts. Floods and landslides killed 433 people and affected 5.4 million people. The Post Disaster Needs Assessment (PDNA) conducted by the UN estimates that the total recovery needs are at USD 4.4 billion. The Killiyar River in Kerala has also been seriously polluted for some time.
Solution / Lesson learned
Integrated Water Resource Management to mitigate future flood risks
Water quality improvement projects have been undertaken by the joint initiative of the Haritha Keralam Mission, the Thiruvananthapuram District Planning Committee, the Jalasree Mission, the concerned Local Urban and Rural Self-Government bodies, and the Mahatma Gandhi Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme (MGNREGS). The project not only addressed the pollution of the river through litter pickup and other activities but also involved tree planting in the watershed and the installation of fences to control litter. The PDNA states that integrated water resource management in this area effectively reduces flood risk through planted trees and better basin ecosystems and should be used as a reference in the recovery of this area.